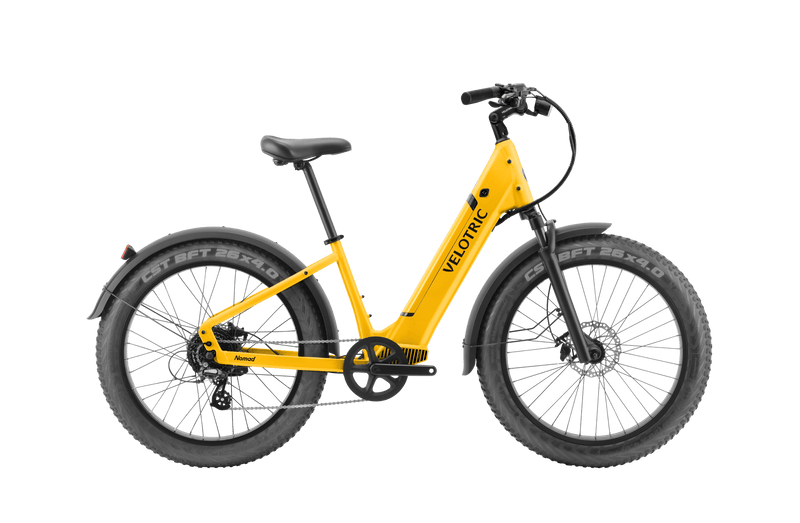
As people search for eco-friendly and cost-efficient ways to get around, they increasingly look to electric bicycles. An e-bike is a practical way to get from A to B. There’s no need to buy gas, parking is zero hassle, and you get some exercise while going about your day.
The thing that sets e-bikes apart from regular bikes is the motor. Powered by a removable, rechargeable battery, the motor assists the cyclist to more easily propel the bike forward. E-bikes can give different levels of assistance while you’re pedaling, and the torque sensor is key to ensuring you get the assistance you need.
The torque sensor determines how much “help” to give you by measuring your pedal power (how much force you apply to the pedal). The more force you apply to the pedals, the more help the torque sensor knows you need.
A torque sensor is an essential part of your e-bike, and it’s worth understanding how it works. This guide will explain what a torque sensor does, why it matters, and basic torque sensor troubleshooting.
What is a torque sensor?
Every e-bike has a pedal assist system (PAS). When engaged, the PAS amplifies your pedaling so that the bike can go faster at a more consistent, smoother pace. A standard PAS has multiple levels; the Velotric Discover 1 and Nomad 1 e-bikes have five-level pedal assist. At the lowest PAS level, the motor will provide less support while pedaling. The motor will provide more support as you upgrade to higher PAS settings.
The torque sensor measures how much pressure you’re applying to the pedals in real time and adapts the amount of power assist accordingly. At low pressure, the torque may amplify your pedal power by 50%. Applying more pressure can amplify your pedaling by up to 300%, depending on the e-bike. Torque sensors are incredibly refined to respond to your pedaling and can take up to 1,000 measurements per pedal stroke.
There are two main types of e-bike torque sensors: rear torque sensors and bottom bracket sensors. Rear torque sensors use a precision strain gauge. Every time you push down on the pedal, the strain gauge moves. The gauge’s movement signals to the motor the amount of force you’re using.
A bottom bracket sensor uses magnets instead of a gauge. The metal shafts between the bike’s cranks have magnetic power, and the sensor assesses the magnetic field around the shafts as they move. This reading is then converted into a voltage signal and communicated to the motor.
What is the difference between a torque sensor and a cadence sensor on an e-bike?
Another type of pedal assist sensor found in e-bikes is a cadence sensor. Both cadence sensors and torque sensors respond to rider pedaling, but how they respond is drastically different.
A cadence sensor is similar to an on/off switch. When you start pedaling, the cadence sensor turns the motor on. When you stop pedaling, the cadence sensor turns the motor off. A cadence-based sensor only measures if you are pedaling, not how hard you are pedaling. To adjust the actual level of motor assistance, you have to change the pedal assist level manually.
A torque sensor, on the other hand, tells the electric motor both if and how hard you’re pedaling. The motor automatically adjusts the pedal assist level in response, boosting your pedaling speed or pushing with less power without requiring manual adjustments.
Why are torque sensors important for e-bikes?
Most basic e-bikes have cadence sensors, while advanced e-bikes utilize torque sensors. Torque sensors are considered superior technology for e-bikes because they offer a more natural cycling experience. They’re also more efficient, automatically increasing and decreasing assistance levels instead of waiting for the cyclist to remember to change the pedal assist.
The benefits of using torque sensors in e-bikes
When buying your first e-bike, consider whether a torque sensor will fit your needs. Although a basic bike with a cadence sensor may be cheaper, torque sensors offer various benefits, including:
- Less manual labor. A torque sensor bike lets you control the bike’s speed simply through your natural pedaling power. It requires far less manual adjustment with PAS controls, offering a more intuitive experience.
- Save battery power. Torque sensor bikes generally use less battery power, giving them a longer range (how far you can ride before recharging the battery).
- Smoother ride. Bikes with only cadence sensors tend to have a more jerky ride. Also, there is often a lag when switching between pedal assist levels. The torque sensor creates a more natural, smoother riding experience.
That said, torque sensors have drawbacks too. It’s usually harder to reach top speeds on a torque sensor bike, and sustaining a maximum speed requires more continual pedal power. That means more effort on the cyclist’s part.
What is the best e-bike torque sensor?
So, which type of torque sensor is best? Although both rear torque and bottom bracket sensors are good, bottom bracket sensors are generally more challenging to repair (more on that below).
The sensor system is only one consideration when buying an e-bike, however. You also want to consider what level of pedal assist and throttle assist the bike offers. Both of Velotric’s class 2 e-bikes, the Nomad 1 and Discover 1, come with five-level pedal assist and throttle assist.
Torque sensor maintenance and troubleshooting
Torque sensors aren’t foolproof and can experience technical issues with time. The following are some signs that your torque sensor may be having problems:
- Slow starts. If you notice a lag when you try to start your bike’s motor by pedaling, the torque sensor may be to blame. The bike’s motor should engage as soon as you apply pedal pressure.
- Sudden stops. If the torque sensor is faulty, the e-bike motor may suddenly stop while you’re still pedaling. This is likely because the sensor isn’t properly measuring the pedal output from your feet on the cranks. It might even feel like someone is pulling your bike back.
- A loud motor. E-bike motors are generally quiet. If you notice your motor getting louder when switching speeds, this may be due to torque sensor issues.
If you notice signs of torque sensor issues, it’s best to have an e-bike professional diagnose the problem. Depending on the issue, the solution could range from recalibrating the torque sensor to adjusting the strain gauge to full replacement.
The process for replacing the torque sensor varies by type. For a rear sensor, you have to remove the rear wheel and battery. For a bottom bracket sensor, you need to remove the battery, left crank, and chainring set. Either way, you’ll need specific bike repair tools, which a pro will have.
Shop top quality e-bikes from Velotric
A torque sensor can help ensure a smooth ride on your electric bike by adjusting the motor’s power to your pedaling effort. That said, a torque sensor is only one factor to consider when buying an e-bike. You also want to look at details like the e-bike’s motor power, braking system, bike wheels, frame type, and more.
Velotric offers a range of e-bike models from mountain bikes to commuter bikes to cater to different cycling needs. The fat tire Nomad 1 can take you for an off-road adventure, while the Discover 1 will make you love your daily commute.
Both of Velotric’s class 2 e-bikes come with comprehensive motor assist functionality, including a PAS and throttle assist. Other high-quality features include high-speed Shimano disc brakes and a Underwriters Laboratories-certified battery (UL2271) with a single charge time of just six hours. Additionally, Discover 1’s Step-Thru model is already UL2849 certified while Nomad 1 is currently undergoing this certification.
For either bike, choose between a high-step or step-thru frame. The high-step frame is best for riders from 5’1” to 6’4”, while the high-step frame is best for riders from 5’6” to 6’9”.
Which bike is right for you? Schedule a test ride to find out.